Ethereum is a global network, that enables users to build decentralized applications with the help of smart contracts.
In the centralized Internet that everyone uses today, users interact with servers hosted by single companies, leaving room for censorship, downtime, and manipulation.
Ethereum solves this problem by hosting its applications on a blockchain that is stored and maintained by thousands of neutral volunteers spread all around the world.
This makes Ethereum a hub for decentralized applications that are highly reliable, uncontrolled by governments, and unmanipulatable.

The Ethereum blockchain also powers its own cryptocurrency called Ether (ETH) which can be used to transact money just like Bitcoin. In addition to simple payments, Ether is the money of all applications on Ethereum. This means that every user of Ethereum needs Ether to pay fees for using any application on Ethereum.
Ethereum's cryptocurrency Ether has become the second-biggest cryptocurrency by market capitalization after Bitcoin, and is of the best-performing investments of the past decade.
| Name | Ethereum |
|---|---|
| Symbol (Ticker) | ETH |
| Price | 2941.47$(+0.73% 24h) |
| Market capitalization | 355,130,537,756.2,999$ |
| All time High | 4946.05$ (Aug 24. 2025) |
| All time Low | 0.432979$ (Oct 20. 2015) |
| Tradable on |
Benefits of Ethereum
Ethereum invented the concept of programmable blockchains, meaning: Users can build anything on the Ethereum blockchain and automatically benefit from the high security of the Ethereum network without having to create a new blockchain themselves.
By allowing anyone to build truly decentralized applications, many interesting and complex financial use cases emerged on Ethereum that are said to have the potential to revolutionize our financial world.
Custom Crypto Tokens
Before Ethereum, creating your own crypto coin would require you to build your own blockchain and a network of users, which is unfeasible and completely inefficient.
With Ethereum, anyone can program and launch their own custom crypto tokens directly on the Ethereum blockchain with a large network of users.
Custom tokens on Ethereum automatically benefit from Ethereum's security and decentralization and can be integrated into all Ethereum applications.
Most of these custom crypto tokens on Ethereum provide benefits for single applications. For example, the token of a social media platform built on Ethereum could allow users to promote their posts, or be used to tip other users on that platform.
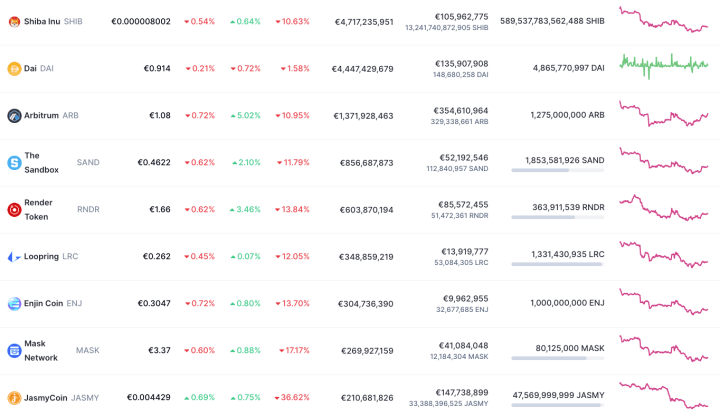
Because these tokens are all on the Ethereum blockchain, users can transfer, trade, and use those crypto tokens in all sorts of applications built on Ethereum, which creates a fully open market. This allows Ethereum tokens to develop a price on the global Ethereum market, similar to how stocks develop a price on the stock market.
To transfer or use any custom token on the Ethereum blockchain, users need to pay fees in the form of Ethereum's own cryptocurrency Ether. This means that if you invest in Ether, you automatically invest in the entire ecosystem built on Ethereum.
Ethereum Decentralized Apps (dApps)
Ethereum allows users to build apps on its blockchain, which are referred to as decentralized applications (dApps). These can be common applications such as games or social media platforms, with the specialty of being hosted on the globally distributed Ethereum blockchain instead of a centralized server of a company.

The use cases for dApps are endless, but here are some exemplary industries that could be revolutionized by dApps built on Ethereum:
Finance: By removing the necessity for third parties with the Ethereum blockchain, financial dApps (DeFi) can replace traditional finance (CeFi) applications, such as banks, brokers, payment providers, and more
Gaming: Ethereum-based games allow players to truly own their in-game assets on the blockchain. Traditional games however can take away the valuable in-game assets of users with a single click.
Social Media: Ethereum-based social media platforms are free of censorship and allow users to earn cryptocurrency for creating and sharing content.
Supply Chain Management: dApps like VeChain use Ethereum's blockchain to track and verify the authenticity of products, improving supply chain efficiency and reducing fraud.
Music and Creative Industries: dApps allow artists to distribute and earn revenue from their music directly through blockchain technology, without having to pay a third party such as Spotify a revenue cut.
There are countless more use cases for Ethereum dApps that are actively being developed, that can be tracked on websites like dappradar.com .
Ethereum DeFi: Decentralized Finance
Decentralized Finance on Ethereum refers to finance-related applications that run completely without middlemen or trusted parties, directly on the Ethereum blockchain.
DeFi is the complete opposite of centralized finance (CeFi), e.g. banks, payment providers, and online brokers, which are middlemen that you have to entrust your funds.
In today's world, banks control users' funds, markets are closed on weekends, wire transfers are expensive and can take up to a few days, and having a simple bank account is far from common in developing countries.
On Ethereum however, users use financial applications reliably and permissionlessy on the blockchain in an instant time all around the clock, and no one can stop them from doing so. The only thing you need to participate in Ethereum's global market is an internet connection and some Ether.
There are DeFi applications of all kinds on Ethereum, ranging from decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges (DEXes) to marketplaces, payment providers, lending platforms, auctions, and more.
Benefits of Decentralized Finance on Ethereum
🔍 Transparent: Anyone can verify what an application on Ethereum does in the background, and that it's not malicious.
🛡 Secure at the core: Due to the nature of the blockchain, it's nearly impossible to truly hack and manipulate an application on Ethereum, which is essential in the world of finance.
⚡ Always available: Unlike traditional markets, the Ethereum blockchain is up 24/7, including weekends and holidays. If you choose to sell some tokens on Ethereum over Christmas or lend some money in the form of Ether on a Sunday, you can do so instantly.
🎭 Uncensorable: Because there are no banks involved, users on Ethereum can transact $1.000.000.000,00 just as easily as $1 with any other person on the globe, without having to provide any personal information.
Decentralized finance applications on Ethereum integrate all custom tokens on Ethereum, forming a modular ecosystem with endless possibilities.
Ethereum DeFi Example
One popular DeFi application on Ethereum is the Uniswap exchange, which allows users to exchange cryptocurrencies of any volumes directly on the Ethereum blockchain without having to trust external companies.

In the screenshot above, a user of Ethereum could trade his 10000 Ether coins for ~18 million US-Dollars in almost an instant time directly on the blockchain, without having to provide any of his private information and without anyone being able to hinder him.
While everything has its pros and cons, DeFi on Ethereum gives people back control over their money, even while using it in highly complex financial applications.
How does Ethereum work?
Just like Bitcoin and most other cryptocurrencies, Ethereum is based on a globally distributed blockchain to keep track of what exactly is going on in the Ethereum network.
The Ethereum blockchain is a publicly visible database stored on thousands of nodes all around the world that documents all transactions that ever occurred on the Ethereum network in the correct order.
Because Ethereum is based on a blockchain, transacting with other users on Ethereum is done fully through asymmetric cryptography that involves no middlemen.
Ethereum's blockchain not only stores transactions of users transferring Ether but also transfers of other custom tokens or user interactions with dApps on Ethereum.
By storing everything that's going on in the Ethereum network directly on an immutable, secure blockchain, Ethereum is resilient to tampering and censorship. Once a transaction is recorded on the Ethereum blockchain, it cannot ever be modified or deleted, providing a high degree of trust and transparency.
Ethereum Smart contracts
To support all sorts of custom applications and not just simple money transfers, Ethereum implements smart contracts, which are computer programs developed by users that are hosted directly on the Ethereum blockchain.
Smart contracts are self-executing computer programs that automatically enforce the rules and conditions of an agreement on the Ethereum blockchain. Smart contracts ensure that users on Ethereum transact according to the rules of an application. They are the judges and the executors of Ethereum.
All applications on Ethereum are built with smart contracts whose conditions and rules are publicly visible. This makes Ethereum work on an "If A then B"-basis just like a vending machine that spits out an item only if you throw in a coin, making third parties obsolete.
Ethereum Smart Contract Example
Imagine Alice wants to sell her rare crypto token on Ethereum to Bob for $10.
The problem: Alice and Bob don't trust each other, so Alice is hesitant to send her cryptocurrency token to Bob first, in fear he may not send the $10 in return.
Alice simply creates a smart contract on the Ethereum blockchain that defines the following rules:
If Alice locks her token in the contract and Bob locks his $10 in the contract, the smart contract will automatically transfer Bob's $10 to Alice and Alice's crypto token to Bob
If Alice or Bob refuses to lock their asset to the contract, the other person can unlock their asset at any time
Unlike in the real world, this contract is not enforced by courts, but directly by a computer program on the blockchain.
This simple smart contract allows Alice and Bob to make a fair trade directly on Ethereum without having to trust each other and without the involvement of a trusted middleman.
In practice, smart contracts on Ethereum are very complex and make up entire applications (dApps, DeFi) on the Ethereum blockchain.
By relying on strictly programmed smart contracts, everyone using applications on the Ethereum blockchain is forced to follow their rules. In such a world, third parties like banks and online brokers are completely obsolete.
Ethereum EVM
When interacting using dApps on Ethereum, the underlying smart contracts need to be run on a computer to do their work, similar to how your operating system (Windows, Linux, MacOS) executes programs on your computer so you can interact with them.
Because the Ethereum blockchain is not stored on a single computer but is governed by thousands of smaller computers - the Ethereum nodes - they all need to run smart contracts on their computers in order to update their local version of the Ethereum blockchain.
To make the conditions for smart contract execution identical for all Ethereum nodes, all nodes on Ethereum execute smart contracts on the Ethereum virtual machine, the EVM.
The EVM ensures that smart contracts run reliably and identically on all Ethereum nodes, despite them having different hardware.
Furthermore, the Ethereum virtual machine isolates the execution of smart contracts from the rest of the operating system, protecting the Ethereum nodes from attacks by maliciously programmed smart contracts.
From a technical perspective: Ethereum users program smart contracts with the Solidity programming language, which then gets compiled to Ethereum bytecode that can be run reliably on the EVM.
Ethereum Gas
Because every single Ethereum node has to run smart contracts each time users interact with one, it's obvious that using applications on Ethereum cannot be free of charge and needs to have certain limits.
Ethereum implements a fee mechanism referred to as gas, which strictly defines the price users have to pay to use applications on the Ethereum blockchain. This gas price for using Ethereum is always paid in Ether, Ethereum's native cryptocurrency.
Each EVM instruction has a specific gas cost associated with it, meaning that users of Ethereum see predictable prices that using Ethereum dApps will cost them.
Depending on the busyness of the Ethereum network, different gas fees have to be paid, which you can track on sites such as etherscan .
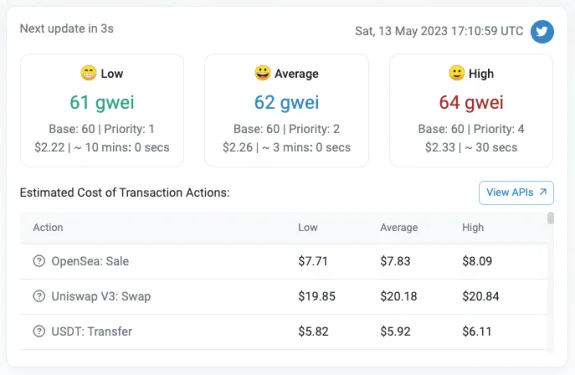
If there was no gas on Ethereum and executing smart contracts was free, users could spam Ethereum with highly computer-intensive tasks that would eventually crash this global network of computers.
Ethereum Proof of Stake
In Ethereum, users who lock at least 32 of their Ether for a certain amount of time can participate in the validation and creation of new blocks for the blockchain. This so-called consensus mechanism of Ethereum's blockchain is called Proof of Stake (PoS).
Ethereum staking fulfills the same role as Bitcoin mining in the Bitcoin blockchain, and that is extending the current blockchain by new valid blocks in a secure and predictable manner.
Unlike the energy-consuming Proof of Work (PoW) mechanism used in Bitcoin mining, staking Ethereum consumes little to no energy and is the reason why Ethereum is often referred to as a more environmentally friendly and sustainable cryptocurrency than Bitcoin.
Nodes of the Ethereum blockchain that stake at least 32 ETH in order to participate in the block creation are called validator nodes. Validator nodes are more or less randomly chosen by the protocol to create and propose new blocks for the blockchain.
Whenever a validator node gets selected to create a new valid block for the Ethereum blockchain by staking its Ether, it receives a reward in the form of newly created Ether coins.
Once an Ethereum validator node creates a new block with valid transactions, it shares it with other nodes that validate the block, and if valid, add it to their local copy of the Ethereum blockchain.
Should a node choose to create invalid or malicious blocks, other nodes of Ethereum will reject the block, and the validator node will be punished by the Ethereum protocol and lose some of the Ether it was staking.
Profit from Ethereum Staking
Even though most Ethereum users either do not have 32 ETH, normal users on Ethereum still have the option to benefit from Proof of Stake by dedicating their ETH to so-called staking pools.
After dedicating Ether to a staking pool, the Ether coins are staked by a validator node, which in return distributes the generated Ether rewards back to the participators of the pool.
By staking any amount of Ether in staking pools, you can earn passive rewards that can be seen as interest on your Ether. Currently, the rewards ETH staking rewards are ~7% per year.
The easiest way to stake your Ethereum without having to run a node is on crypto exchanges, but there is also a growing number of staking pools for more advanced users.
Ethereum Development
Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum is actively being developed by developers of the Ethereum Foundation, with the goal of making Ethereum a global computer that is able to power affordable decentralized applications at a high scale.
Because of the popular blockchain trilemma, Ethereum can only achieve two out of the three traits: security, decentralization, and scalability. The current pain point of Ethereum is scalability, a simple DeFi transaction on Ethereum costs roughly 3-100 US-Dollars depending on the busyness of the network.
To make Ethereum accessible to users of all kinds, Ethereum focuses on developing so-called Layer-2 solutions (rollups and zk-rollups) that are only slightly less secure than the main layer of the Ethereum blockchain but allow for incredibly affordable transaction fees of $0.001 or less.
The exact Ethereum roadmap is subject to frequent changes as the dynamic world of crypto comes with changing priorities. However, the long-term vision remains clear: to build a decentralized and scalable global blockchain with a wide range of use cases.
Future Outlook
If Ethereum is successful in scaling, the future looks bright for this decentralized computing platform as the unique selling proposition of most competitors of Ethereum is better scalability.
With its decentralized applications, Ethereum has the potential to transform a wide range of industries and become a critical infrastructure for the global economy.
Whether it's enabling decentralized finance and banking the unbanked, powering the next generation of social networks, or creating new markets for digital assets, Ethereum plays a significant role in shaping the future of the Internet and global finance.
